Articles For User Experience Designers & User Researchers
-
0 How To Perform User Research Online
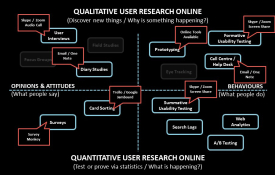
User Research Online Infographic How do you perform User Research remotely? User Research is best performed within the proximity of real users because you get to see the behaviours and emotions away from the screen. When you cannot get to users physically, how can you perform User Research? Fortunately there are ways around this and although these methods and tools are all online, you will have to accept that workshops and sessions will not have that human interaction element. Some things will be lost but you have to make the most of what you can. Collaborate Online Online collaboration is now a top priority for businesses, so User Researchers must adapt to new ways of working. Even though you are not able to be in the presence of the user, there are ways to perform interviews, run moderated usability tests and gather insights. Here are some tools that can help... User Research Tools One Note - Good Dictation Feature Google Jamboard - Collaborative Whiteboarding Evernote - Great Tagging Feature Skype - A Popular Platform Zoom - Reliable Video Conferencing Google Meetings - Another Popular Platform Learn, Streamline And Adapt Learn, streamline and adapt your workflow process by using these tips, tools and techniques to target user insights… Scope and plan your research. Organise your folder structures Try to facilitate productive and collaborative online meetings Use a headset to free your hands up for taking essential notes How Do You Present Your Findings? Microsoft PowerPoint is probably the best way to present your User Research findings to your team and high-level stakeholders. Whatever you use, make sure slides are clear, simple and easy to digest. Use Good Tech Make sure you use good equipment and are on a good connection. There will be problems so just be prepared for anything. Work In A Nice Environment Make sure you have your comfortable workspace area and all of the things you need at hand. If you are making zoom or skype video calls make sure you haven't got anything silly in the background. #uxresearch
-
0 User Research Never Proves, Instead It Reveals
Never "Prove", Always "Support" A science test never "proves" a theory to be true, only evidence supports the theory. A detective can "prove" a criminal committed an offence, only details gathered after the event has passed support the theory. They are from multiple viewpoints based on many perceptions or clues. User Research Never Proves The fact that we try and prove things are happening is because we want to be right. We are all problem solvers and want to get to the solution, it is a habit engrained in us as humans. Even we cannot "prove" something if we have not got the evidence to support the so called "proof". As User Researchers we always have to challenge our own assumptions with the team and not try to "prove" our assumptions but gather evidence to "support" the theory. User Research Reveals Only by continually testing can you find out or reveal "why" and "what" is happening. We are not looking for users to blame or expose being at fault, but to gather findings or evidence to "support" "why" and "what" is happening. There should be a shared understanding amongst the wider team as "UX is a team sport" and we all need to understand user behaviour for the solution to be successful. Do not try and "prove" anything and be open to be challenged on your assumptions!
-
0 3 Personality Types That Will Never Understand User Research
Personality Disorders If you are working as a User Researcher with any of these types of personality disorders within the team, be prepared for difficult times ahead. Talking from experience these types of personalities will never understand User Research because they all lack empathy, the ability to understand and share the feelings of another. 1. Narcissistic Personality Disorder NPD is a mental condition where people have an inflated sense of their own importance, a deep need for excessive attention and admiration, troubled relationships, and a lack of empathy for others. 2. Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) BPD is like having no emotional buffer. It can go from nothing to sudden extremely overwhelming emotions making it a struggle to express them healthily. 3. Histrionic Personality Disorder (HPD) HPD depends very heavily on being noticed, or seeking approval so much that it affects day to day living. This may include being the centre of attention, entertaining people constantly, feeling dependent on the approval of others, making rash decisions or being dramatic and over emotional. Empathetic Personalities Understand Empathetic people are very sensitive, naturally giving, spiritually open and good listeners. They absorb people's emotions and are highly attuned to other people's moods, good and bad. Many empathetic people are introverted, highly intuitive and need alone time. When performing User Research try to work with empathetic personalities as these are the kind of people who can grasp the perspective of the way other people feel.
-
0 What Skills Do You Need To Be A User Researcher?
Observation Probably the most important skill to have as a User Researcher is observation. The ability to spot user behaviour when they are performing tasks is essential. Note Taking Being able to take quick notes and tidy them up later will definitely help any budding User Researcher. Organisation Being organised is crucial to success because you will be dealing with a lot of different types of data and need to refer back to it later. So get your house in order. Presenting Being able to sum up what you did, how you did it and what you found on a few slides out is basically all you need to make good presentations. Patience Depending on the maturity of the UX Practice within the company there will be a lot of times when User Research is overlooked. Try to be patient and introduce small changes. Passion For the same reason as patience, you will need passion to help drive those small changes through. Be bold, but be careful. Practice Being a User Researcher is a full time learning job. You will never know it all and will constantly be learning. Things will go wrong, just like they do in usability tests, but that doesn't mean you should give up. #uxjobs
-
-
0 Virus Causes Spike In User Research Across The Globe
Continuing on from my other article "Social Distancing Prompts On The Fly User Research". The "unprecedented" scale of the "COVID-19" "Coronavirus Pandemic" has forced all countries to learn to adapt and live with the "virus", until a "vaccine" is found. Social Distancing Measures From 1m to 2m, social distancing guidelines, "guided by the science", have forced businesses to adapt queues, entrances and exits, employ more staff and disinfect premises. Travel & Leisure From how people commute on trains, planes and boats, to how people check in at a hotel and go sunbathing on the beach. The "new norm" has caused a massive spike in User Research across the globe. User Research Opportunities There should be even more opportunities for User Researchers in the fall out of this pandemic. Companies across the globe will have to adjust and will need User Researchers to improve and provide even more "unique experiences". #uxresearch
-
0 Why SEO Is Important To Users & User Researchers
Awareness If you look at a customer journey map you will see that the first stage or phase is awareness. How will users find your website? What are the touchpoints? What are the opportunities? Search Obviously search will be one major touchpoint that helps users find your website. But what will the user be searching for and do you have that information on your website? Is it easy to find? Is your content answering a question or solving a problem for the user? These are the sorts of questions you need to ask in order to provide relevant content to your users. So how do you go about making your website searchable? Of course you need to structure your pages so that googlebots can read them otherwise your site will be hard to index. HTML Title Tags These days people tend to search in a "long tail query" fashion. Meaning that instead of typing one or two keywords, they will type a whole sentence and expect that google search experience and response. The HTML Title Tag is the first thing the user sees in search results. HTML Title Tag Example Title Of Your Website Page HTML Meta Tag Description HTML Meta Tag Descriptions are the second thing the user sees in search results. The HTML Meta Tag Description in the html pages tells google what to display on search engine results pages directly after the title. They can be tailored to answer the user question, provide a solution or reveal valuable information that the user needs. Meta Tag HTML Example Google "Crawling can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. Be patient and monitor progress." Google Search Console Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site's presence in Google Search results. URL Inspection Tool Use the URL Inspection tool to request a crawl of individual URLs. If you have large numbers of URLs, you should submit a sitemap instead. To submit a URL to the index: Inspect the URL using the URL Inspection tool Select Request indexing Note: Requesting a crawl does not guarantee that inclusion will happen instantly or even at all. Googles systems prioritise the fast inclusion of high quality, useful content. Ping Tool Send a GET request in your browser or the command line to this address, specifying the full URL of the sitemap. Be sure that the sitemap file is accessible:http://www.google.com/ping?sitemap= Example: http://www.google.com/ping?sitemap=https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml Insert the following line anywhere in your robots.txt file, specifying the path to your sitemap. Google will find it the next time they crawl your site: Sitemap: http://example.com/my_sitemap.xml Sitemap Notification Your Sitemap has been successfully added to our list of Sitemaps to crawl. If this is the first time you are notifying Google about this Sitemap, please add it via http://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/ so you can track its status. Please note that we do not add all submitted URLs to our index, and we cannot make any predictions or guarantees about when or if they will appear. Search Filters How do you check on your website to see if Google has you indexed? You can use symbols or words in your search to make your search results more precise. See Google’s indexed articles of a site by typing "site:" in front of the site address in Google Chrome address bar. e.g. site:yourwebsite.com or site:yourwebsite.com/folder/ Google’s Cache See Google’s cached version of a site by typing "cache:" in front of the site address in Google Chrome address bar. Local Google Chrome Cache In some experiments I have undertaken in this area, there seems to be a random display of newly indexed pages. Sometimes they show up and then they disappear. This might be something to do with your local browser cache, but I am not totally sure. Patience I know it can be quite frustrating when you work on pages and are waiting for ages for them to index, but unfortunately there are many other submissions going on, I can't image the volume. #uxdesign #uxresearch
-
0 A List Of Useful Psychology Books For User Researchers
Flow: The Psychology Of Optimal Experience Creative Change: Why We Resist It . . . How We Can Embrace It Getting To Yes Getting Past No: Negotiating With Difficult People Surrounded By Idiots Mental Models: Aligning Design Strategy With Human Behavior The Secrets Of Consulting: A Guide To Giving And Getting Advice Successfully Influence: The Psychology Of Persuasion Pre-suasion 100 Things Every Designer Needs To Know About People Perfect Phrases For Dealing With Difficult People Brilliant Communication Skills
-
0 Why is Customer Experience So Important?
Customer Experience is contact with a product or company whether that be inbound or outbound. It is dependent on delivering effortless customer journeys that are personalised and proactive whilst maximising company productivity. In these times we don't usually have the comfort of speaking to someone when we want a product or a company service, many customers shop online, so the main touchpoint of any company usually begins online. With customers engaging with your company over multiple channels — web, chat, email, mobile and social — a focus on customer experience is more critical than ever to gain a competitive advantage and for the longevity of any business. Journeys / Touchpoints What might be considered critical by a company may be far from the experience expectations of a customer. Companies sometimes overthink the user journey and add unnecessary complexity that can quickly trip up the customer and causing a bad experience. In order to better identify and align each customer touchpoint with the business expectations, the integration and automation of customer information from back office systems into contact centres helps a company streamline the customer experience. It provides agents and representatives with preemptive knowledge – from multiple sources – to get a holistic view of each customer’s expectations when they engage with a company. Central to this strategy is the ability to meet your customer expectations, understand the context of each interaction across all channels, optimise the routing of customers and how to best leverage customer feedback with detailed analytics to achieve better results. Essential Elements These core elements provide the engine needed to create a view into the customer journey, with process refinement and intelligence to power great customer experiences. The business advantage to meeting a customer expectations with great customer experiences will ultimately drive higher revenues, lowers costs, improve efficiencies and create happier employees! Well-Designed A company website is usually the first place customers look for information about a shipment, a return policy, or even how to contact, and a well-thought-out FAQ section can save employees the hassle of answering routine questions all day. Accessibile If your customers can’t contact you easily, then your customer service isn’t as good as it should be. As was mentioned above, having a good website is crucial. Your contact information should be clearly displayed on your website, alongside your hours of operation. If a customer has to search for too long for information on how to contact you, when they finally do get you on the line, they’re already going to be disgruntled. Quick Response Customers hate waiting. Especially in today’s instant-gratification-oriented society, if a customer has to wait for too long for a response, they’re going to become unhappy. A quick response time to emails and phone calls (and a sincere apology on the rare occasion when you’re unable to be prompt) keeps customers satisfied. Empowered Employees If your employees do not have the ability or the permission to solve a customer’s problem, you are creating a recipe for awful customer service. If you don’t feel comfortable allowing your customer service representatives to make small decisions without having to answer to a supervisor for every choice they make, then you don’t trust them. And if you don’t trust them, then they probably shouldn’t be employed by your company. Thick Skin In order to deliver great customer service, you’re going to have to change the way you look at mistakes and criticisms. Instead of getting offended or defensive, try to view these inevitabilities as opportunities. Every mistake or bad review is another opportunity to fix something that was previously broken in your company. Take advantage of it. Surprise Surprising your customers is a great way to make a good impression. There are many ways to surprise your customers with something meaningful to them. For example, if you recently solved a complaint with a customer, consider following up with a gift card or credit on their account without giving them any notice beforehand. This is a small step, but because it’s so unexpected, it will make a big impression and will show the customer that you care about their needs. Trust Trust in your customers. Too many companies in today’s business world operate under immense paranoia. They assume that every customer is trying to game the system and that if they let their guard down even momentarily, they’ll find themselves out of business and out of money. This simply isn’t true. Most customers who need your help have legitimate complaints and just want their issues addressed with as little hassle as possible. If you trust them, then you can give them what they want and save both of you time and stress. Responsibility Everyone knows that they need to stand behind their products and services, but there are other aspects of a business that are probably overlooked the need for which to take responsibility. Customers expect continuity, and failing to provide them with that continuity will make them dissatisfied. In the customer’s eyes, your company and your partner/ manufacturer/ distributor are one and the same. But customers gave you their money, so they expect you to take responsibility for their service, not place blame on some third party that they don’t know anything about. Recognition One of the most important aspects of CX is making sure that your customers feel appreciated. The key here is sincerity. Recognize their efforts in a sincere way. Post a message at the bottom of your website for a day, send them a handwritten thank-you card, or send them a small gift card – anything that will show them that you appreciate their help. Patience Some customers simply are not worth the business they provide. Some customers are bad people. Despite your best efforts, they’ll whine, complain, curse, write bad reviews, demand free products or services, make unreasonable requests, and generally make your life a living nightmare. Recognizing this and learning how to drop the lost causes while still focusing on those customers who actually deserve your time will save you a lot of stress. #cx #ux #businses
-
0 How To Use Practical Job Mapping To Uncover Unmet Needs
So Many Different Users There may become a time when there are so many different users. You just simply cannot narrow them down to the recommended 5 personas. The users share similar needs and there is little distinction between them making it hard to focus on a main persona. However, you may know what jobs, tasks or goals they need to achieve. So what can you do instead? Practical Job Mapping In Practical Job Mapping there is no single user persona, but instead a job or task executor who goes through specific steps to complete a job, main task or goal. The job or task executor will perform smaller steps, jobs or tasks in order to complete a main job, task or goal. It is the smaller steps, outcomes and unmet needs that is the focus of Practical Job Mapping. You work with the user and go very slowly over every single step they take when trying to achieve the job, main task or goal. You separate them out into recognisable stepping stones along the job, main task or goal. When you do this you can find workarounds, unmet needs and opportunities for improvement. What is important to note is that you should really do this with a few users just to validate the same things are happening at a larger scale with more users. #uxresearch
-
0 A Guide To Facilitating Group Harmony In Workshops
Group Harmony Workshop Facilitation Workshops are a useful tool in the design process, but mistakes will happen if the facilitator has not prepared the ground rules. It could cause workshop participants to waste time and encounter problems. In order to allow people to work together more productively, create a safe space in workshops by negotiating a Group Harmony. A Group Harmony is a manifesto or set of guidelines that sets the tone for how people will behave within workshops. Some examples of this might be... Allow everyone the opportunity to contribute Understand where people are coming from, even when they disagree Be respectful to workshop participants Be open to options and feedback Have fun but stay focused Build on each others thoughts and ideas Everyone has a voice Refrain from mobile phone or laptop use Do not be afraid to ask questions A Group Harmony workshop facilitation only works if it is agreed by the group. Group Harmony should be proposed and agreed by participants and not imposed upon them. Things That Group Harmony Prevents Reasons for the workshops are vague Lack of workshop preparation No measures of success Unclear roles and responsibilities The wrong participants were invited The facilitator lacks influence or authority The facilitator fails to connect and engage participants No pre-defined guidelines are established No next steps are defined Lack of accountability and commitment from participants They are very boring No rest breaks or down time
-
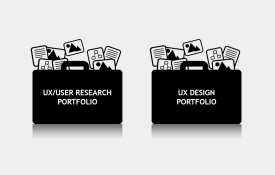
0 How Do You Build A UX Portfolio?
The Purposes Of A UX Portfolio UX Portfolios are built to show skills and work experience to employers or clients through past projects, whether that be commercial or personal. A UX Portfolio should convey the research or design activities undertaken. Basically what you did and how you got to there. There are two types of UX portfolios, a UX/User Research Portfolio and a UX Design Portfolio. But what is the difference between the two? UX/User Research Portfolios A UX/User Research Portfolio should include... Your role and why you were hired Questionnaire, learning, action and approach plans Users, stakeholders and team members you collaborated with Conceptual, mental models and possibly some sketches you produced User or customer journey maps Usability test plans, results and iterations Summary of findings or main takeaways Lessons learned Future Proposals UX Design Portfolios A UX Design Portfolio should include... Your role and why you were hired Design processes and decisions made Users, stakeholders and team members you collaborated with Annotated sketches, wire frames and mock ups you designed User journey maps Usability test plans, results, iterations or A/B test designs Lessons learned Future Proposals Bonus Points For Business Benefits What may also be included in both types of portfolio are the business benefits of the work performed and how it was conveyed to the business as a benefit, or return on investment (ROI). Make Easy To Read, Structured And Usable A UX portfolio should be simple and logical. That means no fancy designs or animations that will distract from the work being displayed. The hiring manager viewing the portfolio will not have much time and will want to get to the guts of the information very quickly and easily. The amount of times I have seen a portfolio that is way over engineered with glossy design and hard to read fonts is unbelievable. Don't do that! #uxdesign #uxresearch
-
0 How To Get Your Questions Answered By Stakeholders
Stakeholders come in all shapes and sizes, from the aggressive to the passive, they all have influence in a project and will have different levels of interest and power. As a User Researcher you will need to interact with every stakeholder on a project, so it is good to have a plan of approach. In this case It's not what you do, it's the way you do it. The Approach Problem Before you setup the meeting invite you will need to prepare some questions you will want to ask. Stakeholders tend to have limited time and are usually very busy, so you will want to approach them in a way that will open them up for questioning, without looking like you will take up too much of their time. You could just send an email with the questions in it, email it to them or send them a meeting request. Either way you will need to be clever with your approach as the way you communicate to the stakeholder will be crucial for further interactions. Change The Approach Frame In a famous past research study some researchers went out and asked stakeholders... "Can I have some of your time?" of which 29% volunteered When they changed the approach question and asked... "Would you say you are a helpful person?" 77% volunteered It produced some amazing results. Asking them if they consider themselves helpful puts them in the frame of mind of being helpful! Critical Questions For Stakeholders As I stated earlier in this article, stakeholders all have influence in a project and will have different levels of interest and power. My last few tips for this article are two important questions you could ask stakeholders... "If you could change one thing, what would that be?" This will tell you what they are really passionate about. "Is there one thing that you do not want to change?" This will tell you what they are really worried about.
-
0 What Does It Take To Make A World Beating System?
A World Beating System Boris Johnson has claimed the UK will have a “world-beating" system to test, track and trace for Coronavirus up and running by 1 June 2020. From early media reports it doesn't look good for this strategy to succeed. User trust as well as speed of build and distribution are hampering efforts. There is lack of clarity and total confusion over what people expect from a world beating system. There rightly seems to be public concern in all areas. Boris Johnson has also claimed "We’ve recruited 24,000 trackers and by the 1st of June we’ll have 25,000." Well as long as they have access to a phone, internet connection and are prepared to watch TV shows on netflix, they're ok. It is great to see how tax payers money is being used. So What Does It Really Take To Make A World Beating System? In the past I have had execs in brainstorm sessions telling me they want an "All encompassing world beating system" which is usually a dream or vision that is practically impossible to start small with. The Coronavirus app is something that has been tried and used before in other countries, but it only really works if you have user uptake and adoption alongside a well thought out support strategy. It entirely depends on the underlying support structure of the strategy as a whole for any system to be "world beating", whatever that means. "World beating" probably translates to "The Best User Experience" and that can only be done with solid User Research with real users to cater for their needs. So what does it take to make a world beating system? Service Design And Service Blueprints A service blueprint is a diagram that shows the relationships between different service components, people, props and processes, that are tied to touchpoints in a customer journey. Service blueprints give an organisation an understanding of its service and the underlying resources and processes seen and unseen to the user that make it possible. Focusing on this understanding provides strategic benefits for the business. It allows visibility of the back stage processes needed to support the front stage activities. Blueprints are treasure maps that help discover weaknesses. Poor user experiences are often due to an internal oversights, a weak link in the system. While we can understand what might be wrong in a user interface, determining the root cause of an issue is much more difficult. Blueprinting exposes the big picture and offers a map of dependencies, allowing a business to discover a weak leak or root causes.
-
0 What Bruce Lee Teaches Us About The Way Users Think
"Don't think! Feel. It's like a finger pointing at the moon. Don't concentrate on the finger, or you will miss all that heavenly glory." Neuroscience Part of the reason the student in this very famous film scene struggles lies in neuroscience. In this branch of “brain science,” there are two types of thinking: System 1 Thinking is reactive; where emotions, habits, and intuition are the dominant traits... Fast Automatic Frequent Emotional Stereotypic Subconscious System 2 Thinking is analytical; deliberate, factual, and logical... Slow Effortful Logical Calculating Conscious Infrequent When Bruce tells the student "Don't think! Feel." he is instructing the student to use System 1 Thinking which is much quicker. The student is somehow made to relax by the words of Bruce when he says; "We need emotional content." pointing at his head to signify to the student to use System 1 Thinking. The student tries again and learns how to switch systems thinking and is amazed by what he has learnt. The student learnt how to use System 1 Thinking to kick quicker. The Way Users Think When asked a question, most users will answer with System 2 Thinking because they are “on the spot” or “don’t really know,” so it’s easier to answer with deliberate and logical answers, i.e., knee-jerk reactions. As we work on a project or win new work, we accept these answers because we don’t want to question the customer. The problem is, most people spend the majority of their time using System 1 Thinking. When someone enters into their world and starts asking questions, they are thrown off, and they answer with System 2 Thinking, leading to answers that are contradictory to their true, real needs. Do Not Listen To Users User Interviews, User Observation, Shadowing and Usability Testing will continue asking questions until we reach the actual underlying needs of the user, and we know we have concluded that when we are dealing with emotions, motivations, and needs. At this stage, we have moved far beyond listening to the customer. We do a huge disservice to users and clients by acting on what they say. Instead, we should seek to better understand what they are actually trying to convey or get done. This is one of the reasons why User Research matters and why we should go beyond the surface and try to uncover the true needs, wants, and motivations that will drive superior results. Don't think what the user is thinking! Feel what the user is feeling. Emotional content. Here is the famous scene from Enter The Dragon...
-
0 How To Improve The Search User Experience
Why Users Search Mostly when users search they are trying to do one of these things… Find a specific document Find a collection of documents Answer a question Find someone Discover something helpful Expectation Users have an expectation of a “google” like search experience when we search using any product. How Users Search The user will start with a question The system will then try to formulate a database query The user will then review the results and filter them to narrow down by specific criteria Expectation The expectation is that users will easily be able to find exactly what they are looking for, just like they do when they do a google search. Keyword Search Challenge The terms users search for are not synonyms, topics or concepts and may not be in the desired documents. Users have a question and the formulation of a query but the system is not intuitive. When document authors create documents they do not think about how someone is going to search for it or the questions that users want to answer. Machines Interpret Search For example when a user searches for…“Pictures of people having fun” The user wants to search to… Pictures: find a picture People: with 1 or more people Fun: labelled as “fun” What Users Want Intuitive experience Ability to ask a question Results that match their intent Relevant results Ability to filter those results Solving The Search Problem What is the user’s intent? What are users searching for? How do they think about filtering? What questions do they want to answer? When you understand user intent the answer you get is subjective so you need to constantly monitor the questions that users are trying to answer so that you can provide the best possible answers. Try To Enrich Metadata Building a pipeline and applying machine learning can analyse metadata and constantly apply changes to improve the search experience. Create Rich Metadata Extract and enrich names, places, sentiments, etc… Standardise and apply industry terminology, catalogue or hierarchy Apply user terminology and translate technical jargon Applying metadata to documents will improve the search experience by making it easier for users to find what they are looking for. This can be done with Machine Learning. Machine Learning Machine learning is a data science technique that allows computers to use existing data to forecast future behaviours, outcomes, and trends. By using machine learning, computers learn without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning solutions are built iteratively, and have distinct phases: Preparing data Experimenting and training models Deploying trained models Managing deployed models How Machine Learning Works Pattern Detection New Signal Identification Weighting Custom Signals Based on Query Image Search Word similarity detection Query Clarification While machine learning isn’t (and probably never will be) perfect, the more humans interact with it, the more accurate and “smarter” it will get. This could be alarming to some – bringing visions of Skynet from the “Terminator” movies – however, the actual result is likely a better experience with technology that gives us the information and services we need, when we need it.
-
0 Test And Trace Strategy: The Importance Of User Trust
The NHS Coronavirus App "We are currently developing our NHS coronavirus app, which is being trialled on the Isle of Wight. When rolled out nationally this app will supplement the other forms of contact tracing." There have been early reports that many users have downloaded the app and are actively participating. Hopefully they are usability testing it and fixing the bugs before they release it and maybe that's why it's taking so long. This is great news and anything that will help to get us out of this situation is a good thing and should be encouraged by us all. Sharing information about your recent contacts "If you get a positive test, we will contact you and ask you to share information about any close contacts you had just before or after you developed symptoms." There is a general concern amongst potential future users that contacts and recent journeys are not something they wish to disclose because they do not know where that data is going to be stored and used. When we contact you "If the NHS test and trace service contacts you, the service will use text messages, email or phone." There is a general concern amongst potential future users that there is no possible way to assure them that they are actually talking to an official NHS representative. What we will ask you "We will ask you to provide, where possible, the names and contact details (for example, email address, telephone number) for the people you have had close contact with." As there is a general concern amongst potential future users about the authenticity of the caller it makes answering questions uncomfortable. How this information is used "Based on the information you provide, we will assess whether we need to alert your contacts and ask them to self-isolate." There is nothing here that gives any assurance to users where their data is stored, how it is shared and who it is shared with. There is also a concern that this data could be used for other means. The Importance Of User Trust Whatever the case, trust is a big issue and one that we should all think about when building products and services for users. If you do not have trust from users it will be difficult to engage. They really need to look at these issues to build confidence in potential future users but I also hope the use of the app and user adoption improves.
-
0 Social Distancing Prompts On The Fly User Research
Planes, trains and automobiles are all needed to keep us moving. At this time of writing, lock down restrictions have been enforced, so all are down and not moving anywhere. The Lock Down Gamble The governments of the world are taking a gamble by slowly easing lock down restrictions. On one side they need to get the country back up and running, but on the other they need people to feel safe and secure. They also do not want a dreaded second wave. We Didn't Know Little did we know that it was going to be a "microbe" and not a "missle" killing thousands of people around the world. Unfortunately due to the lack of insight and preparedness in this area, not one of these companies had a plan for social distancing or have a plan for post lock down recovery. Some have already fallen by the wayside and more will fall. Disaster Recovery It is quite ironic that IT companies have been performing disaster recovery processes for decades, making sure that the data they hold is backed up and safe, just in case a bomb drops. Nobody had a disaster recovery process for a virus pandemic though. Living with a virus that has no cure is going to be a challenge for everyone. Floor stickers, barriers and notices are all there to see these days. They had to be put up in a short space of time. The brute force UX they are employing needs to be done because the planes, trains, entrances, walkways, platforms, aisles and queues are not designed for the "new norm". Companies are having to perform on the fly User Research.
-
0 Being A User Researcher Feels Like Being A Shaolin Monk
At the Shaolin Temple in China, a Buddhist warrior monk faces a test that will change the course of his life forever. The Monkey Going Up The Tree! Sometimes User Research feels like being a Shaolin Monk, especially when it comes to trying to perform The Monkey Going Up The Tree! Dedication We spend years learning our craft and never really stop learning. It's part of the job and something that makes us curious to actually perform User Research in the first place. However, sometimes It can feel that most of our research efforts get lost in the noise of delivery, it can be very soul destroying at times. You have to be patient and celebrate the small wins. On the other hand, It can also feel very elating when we get some new findings from a usability test or stumble on some user behaviours we didn't know about before. Always Learning Either way, being a User Researcher feels like being a Shaolin Monk, because we go through that same life long learning experience, perfecting our craft to achieve greatness. We always strive to get to that apex of the tree like the monkey, rarely does it happen, but that doesn't mean that we shouldn't at least try. It's what makes us better.
-
0 What The Space X Explosion Teaches Us About Usability Testing
Space X’s next generation Starship rocket exploded right after a test at the company’s south Texas test site on Friday 29th May 2020. It was the fourth prototype. Shortly after it ignited the engine on the Space X test rocket developed a fireball which engulfed it in flames, leaving very little standing and causing damage to the test site. What Is Space X Teaching Us? We do not usually get things right first time We need to run a few tests before we launch We need to learn so that it does not happen again So why do Space X do this and how come many public and private sector companies do not do this? In my years of experience, very little Usability Testing occurs in public and private sector companies. This is astonishing because companies spend millions and billions of money on developing software that they hardly test with their users. Usually Testing is usually performed near delivery, when it's too late and nothing can be changed. They usually call this UAT. I ask, what is the user accepting in this test? Off The Shelf Products The reason companies do this is because it is very easy to buy off-the-shelf products, or lift and shift their legacy system, because that is a deliverable solution in a short time frame. Warning! Unless the needs of the user are totally matched and the usability of a good standard, off-the-shelf software is never a good idea. Even if the software is off-the-shelf, how much does it satisfy user goals? It may claim to perform the tasks that the user wants to perform, but how efficient and effective are these tasks? Myth: User Research Will Take Time Of course building a new system and doing the User Research, Paper Prototyping and Usability Testing takes time doesn't it... All of 20 mins to test an idea. Why would you want to do this? LOL The most worrying thing is that many public and private sector companies do not do this! Space X Want To Learn Space X are testing the space rocket not just because it costs a lot of money to build and do not want things to go wrong, they are testing all sorts of other things too because they want to learn. Those test results will probably help them pin point where the failure occurred so that it can be fixed or improved. It is the same with Usability Testing, even though the product may have had a lot of money spent on developing it already and needs to be launched soon, it is probably even more important to test in order to prevent even more money being spent unwisely. But We Use AGILE I call it WAGILE and it is usually a mix of AGILE and Waterfall. Developers want to work in an AGILE way, but Executives want to deliver the way they always have done, the Waterfall way. It is only when this mindset is changed that companies will innovate and become more user focused. Just because you claim you are doing AGILE does not mean you are performing UCD. Unless it is baked into the workflow. Continuous Improvement Tests do not have to stop before launch. They should be continuous. NASA and SpaceX have many tests on the ground and in space.They are constantly testing everything! Things are very light in space and it is a totally different environment, it costs a lot of money to get the stuff up there, so there is a whole heap of testing done on the ground too. When they actually get up into space they need to test more things in order to learn and improve. They will take this test data and use it for future launches, learning and continuously improving. If you or the company you are working at is not doing Usability Testing or not enough of them you must get started now. Usability Testing is not Rocket Science!
-
0 Back To The Future Of Prototyping! Great Scott!
Emmett Brown built a prototype to test and show Marty McFly how to get the DeLorean time machine to travel through time by getting the car up to 88 Mph whilst taking a lightening bolt at a specific time in a short space of roadway. This shows us how prototyping allows us to... Build: Try something out before we actually build it Measure: Validate our assumptions Learn: Take valuable insights from findings Rapid Prototyping (RITE) allows us to do all of this quicker. There are many types of prototypes... Printouts Clickable wireframes HTML, CSS & JS Websites Fully working demos Choose depending on what you are trying to learn. It should be a throw away piece of work just to get an idea of whether things will work or not. "Please excuse the crudity of this model. I didn't have time to build it to scale or paint it." Testing using prototypes is just the same process because you are finding out if the idea will actually work by getting up front feedback as to what needs to be changed or improved. Unfortunately we don't have the luxury of a time machine, but we can make prototypes to test our assumptions and help us keep on the right track to try and change the future outcome.
-
0 Warning! Users Only Have 5 Seconds For Your Product!
How will the user perceive your product in 5 seconds? 5 seconds is probably the most amount of time you have to capture user attention. If it's not obvious then you might be asking too much time and attention by having too much in the user interface for users to take in and no clear visual indicators. A 5 second test can help you see how clear or memorable a product is to users... Print off your screen on paper Find a volunteer Explain you will show them something for 5 seconds Show it to them Commence 5 second countdown Hide it from them Ask what they remember and the purpose Did they get it right? Try someone else Give it a try it yourself. Show someone an idea for 5 seconds, see what they say? It will tell you how clear and easy your design is.
-
0 Why UX Governance is Critical To Company Success
UX is not a new field. You would think that it is by the way people are talking about it! Users, user journeys, wireframes, prototyping, etc... But "talk is cheap" and "actions speak louder than words". "Do! There is no try" and we have to start catering for ever increasing customer/user expectations today. Companies will continue to struggle to cater for customers/users. They will be impatient, time starved and increasingly too busy to fit you into their lives. Agile Release Train The train needs to deliver at the end of the planning period but what is actually on the train? Is it bringing user value and business KPI benefits? Are we delivering the best user experience or are we just delivering something we will "have a look at later"? Output not Outcome The problem is that companies will mostly be focused on delivery (Output), but it is the job of UX professionals to advise on best practices (Outcome). Some may or may not get followed due to "constraints" be that technical, political or otherwise. The results is a "compromised" user experience (Outcome) led by technology and development. These limitations will be hard for companies to overcome. Why does this happen? It happens because there is no UX Governance. There is no authority at the correct altitude for change to affect. 5 KPI Benefits Of UX Increasing Revenue - more user adoption, more conversions, more sales Decreasing Costs - save time and resources on development Retaining Existing Customers - Keeping your users happy helps them come back Gaining New Customers - Good on-boarding experiences and simple user journeys Increasing Shareholder Value - The brand experiences popularity provoking interest The companies that are able to adjust to a user centred way of working will be ahead of the competition. Levels of UX Governance Non-existent - There are no UX people in the company Existant - There are one or two UX people in the company Established - There is a UX team in the company Governed - This is a UX lead company It is only at levels 3 and 4 that any kind of user experience practice will have the authority for change to affect. At levels 1 and 2 the company will be focused on delivery, your efforts are limited by the time needed to deliver and the user experience will be limited too. What level is the company where you are working at? Of course in time we will see more companies adopt a UX Governance, but in the meantime while companies struggle with the change the market for UX has never been so much in demand. Hopefully we will see more companies start adopting a UX Governance as a critical business function.
-
0 How UX Can Influence And Help The Planets Align!
I have often heard office workers say in surprise "the planets are aligned!" like it is so uncommon. Like when a big decision is being made and consensus is some kind of miracle. But it really shouldn't be this way. It is possible to make sure "the planets are aligned" if you have a shared understanding. UX influences and helps the planets align! It does....no joke. Shared Understanding A new knowledge creation influenced by participation and collaboration and achieved by exchanging individual knowing for group knowing, thus changing from individual perspectives to a joint perspective that emerges from collective contributions. Basically a shared understanding is both the individual and collective ownership of a new perspective accepted by the group. Building a shared understanding is not about processes or tools or whether anyone can design or code. Having a shared understanding is about getting everybody to walk in the other person’s shoes for a while. It’s about building respect, vocabulary, and gaining enough insight to build solutions together making a better experience for our users. It’s how we build a good user experience. We seek to understand our users so we observe and study them. How Does UX Influence And Help Align The Planets? With a collaborative approach sketch to visualise the problem, build a shared vocabulary and engage in a process of continuous discovery and learning.
-
0 Why Is It Good To Use Signifiers In Interface Designs?
Signifiers are indicators of any type that communicate the action needed so the affordance (how it works and what it does) can take place, and it’s a term that’s widely used in the field of semiotics. "Semiotics - the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation." Wikipedia Every day examples of Signifiers... "Push and Pull" Door Signs "This Way Up" on boxes "Slide To Open" on phones "Drag Here" to drag and drop "Click and Tap Here" on interface buttons These Signifiers tell us how to use it and if we didn't have these we would not know what to do with it and get frustrated with the experience. Ever walked up to a door and couldn't work out how to get through it? Ever tried to open a box the right way up when there is nothing written on it? Ever wondered why slide to open on phones has an arrow? Where do you drag and drop something if you have no signs? How do you know what a button will do if you press it? Signifiers are an important part of an experience and are there for a reason but not everyone uses them effectively. Hopefully with more awareness of UX our everyday experiences will improve but some experiences are deep rooted and may never be fixed. Try to walk through a door that has no signifiers and think about how it feels!
-
0 Why User Validation Is Your Ammunition
The Problem When you are working with stakeholders and trying to reach consensus, you sometimes get to the point where everything gets pulled apart. If you are working in an organisation that is not particularly "UX aware", the Project, the Plan, the User Interface, the inclusion or removal of elements on a page, all get out of focus and somehow starts going a bit "pear shaped". If your not careful you will be delivering something "Off The Shelf" or "Out Of The Box" just to get it "Out Of The Door" and not thinking if your users will actually be bothered. Oh dear, your shiny new "Portal" does not fit your user needs. So what does one do? Validate Assumptions UX Professionals must try to get validation from users in any shape or form. Testing as soon as possible is crucial to determine if your design fits user needs. But we need a live environment to test and we don't have that, we would have to build it and that will take time. Test To Validate Ideas When the "pear shaped" scenario starts to rear it's ugly head it's time to get validation, and that can only be done by testing. So how do we test? Early testing is great for getting insight at little cost. You don't need budget, resources or meetings to start testing your idea. The Bin Man Testing Approach Sketch a design on A3 design for a desktop view and A4 paper for a mobile view Using a thick marker, sketch your idea in both views Show it to a prospective user for validation and take notes Go back to the design and use those notes to fine tune the design Go back to step 2 and repeat... When the majority of your users give similar positive feedback gives you a good idea your design is going to work. Of course, this is the most cheapest and roughest way of finding validation, but it also shows that it's really only the "idea" we are trying to validate. Other techniques for testing could be sketches on paper, printouts of mocks, click through wire frames, all of which a very low cost and technology independent. In this increasingly technological world we tend to think that computers will solve all our problems, but it's the validated ideas that count, because your team thinks but does not really know what their users want. Your quickest and cheapest options are the approaches I have mentioned in this artcile and I would advise any UX Researcher or Designer, or whoever has what they think is a good idea to use these techniques to validate assumptions. Your Ammunition So what do you do when you finally get this validation? Validation is the ammunition for UX people to help the team understand and respect users, how they perceive things and what they think of the idea. So the "pear shaped" situation could be saved by some validation ammunition in order to shoot down the assumptions the team had about their users. Important! Reach out to your users and seek validation, but remember, they do not have much time for your idea, so you need to make it obvious. Oh and don't forget to offer a gift in return for their time, otherwise they may not be bothered and won't give you useful feedback.
-
0 6 Critical Questions To Ask In A Usability Test Questionnaire
Attractiveness: Overall impression of the product. Perspicuity: Is it easy to learn and get familiar with? Efficiency: Can users solve their tasks with little effort? Dependability: Does the user feel in control? Stimulation: Is it exciting and motivating to use? Novelty: Is the product innovative and creative? Attractiveness is a pure valence dimension. Perspicuity, Efficiency and Dependability are pragmatic quality aspects (goal-directed). Stimulation and Novelty are hedonic quality aspects (not goal-directed). The best point in time to ask these questions to usability test participants is directly after they finished working on the test tasks. If participants fill the questionnaire only after they had a lengthy discussion about the product with the person conducting the test, this will influence the results. The goal is to catch the immediate impression of a user towards a product. Try to get the answers before you discuss with the participants. Some of the participants may be unfamiliar with the special item format of the questionnaire. Mention that this is a scientifically evaluated questionnaire to measure user experience whenyou hand it over to the participant. This will improve the quality and consistency of the answers.
-
0 3 Main Ways Users Search For Information
Search Queries Search queries are the words and phrases that people type into a search box in order to pull up a list of results – come in different flavours. It is commonly accepted that there are three types of search queries... Transactional search queries Informational search queries Navigational search queries 1. Transactional Search Queries A transactional search query indicates an intent to complete a transaction, like making a purchase. Transactional search queries may include exact brand and product names (e.g. “samsung galaxy s3”) or be generic (“iced coffee maker”) or actually include terms “buy,” “purchase,” or “order.” In all of these examples, you can infer that the searcher is considering making a purchase in the near future. Vertical searches are a subset of transactional search queries, and represent people looking to make a transaction in a specific industry. These include local searches, restaurant searches, hotel searches, flight searches, etc. 2. Informational Search Queries When someone enters an informational search query into Google or another search engine, they’re looking for information – hence the name. They are probably not looking for a specific site, as in a navigational query, and they are not looking to make a commercial transaction. They just want to answer a question or learn how to do something. Wikipedia defines informational search queries as “Queries that cover a broad topic (e.g., london or lorries) for which there may be thousands of relevant results.” 3. Navigational Search Queries A navigational query is a search query entered with the intent of finding a particular website or web page. For example, a user might enter "youtube" into Google's search bar to find the YouTube site rather than entering the URL into a browser's navigation bar or using a bookmark. “facebook” and “youtube” are the top two searches on Google, and these are both navigational queries. Keywords Vs Search Queries "keyword" and "search query" are often used interchangeably, but there is actually a difference. A keyword is sort of like the ideal of a search query – it's an abstraction that we extrapolate from multiple search queries. A search query or search term is the actual word or string of words that a search engine user types into the search box. You can think of a search query as the real-world application of a keyword – it may be misspelled, out of order or have other words tacked on to it, or conversely it might be identical to the keyword. Search Engine Optimisation A search engine marketer uses SEO to target keyword abstractions by optimizing on-page content (using the keywords in URLs, title tags, body copy, image file names, meta descriptions and so on), by building inbound links with keywords in the anchor text, etc. Search queries, on the other hand, are the real-world terms that people use to find those pages through paid and organic search. Search queries are a larger set than keywords, and by looking at search queries you can find new keywords to target in search marketing campaigns. Keyword Research Just like with any search optimisation exercise the first step is keyword research. Before you can actually get down to optimising you need to identify the commonly spelled and misspelled terms related to your site. There are a number of ways to do it. Check your website logs Look through the common spellings and misspellings lists Try misspelling words yourself Use a typo generator Keyword Analysis Once you have your keyword list you need to analyse each search term to see if it's worth optimising for. The most important factors you should consider are… Search volume Search suggestion Search competition Keyword Patterns vs User Intent User intent is what the user wanted when they typed their search terms into a search engine. So, instead of using keyword patterns to find keywords with a specific intent, why not just simply pick keywords by the user intent? To get the best results for your campaign, matching intent of users is better than just simply matching keyword patterns. Picking keywords by their patterns is a way to find keywords that have a specific search intent.Matching the correct user intent to what the site is offering will increase conversions.
-
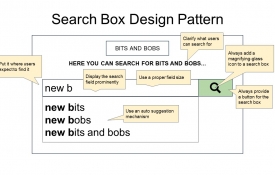
0 Search Box UX Design Pattern Guidelines
The search box is one of the most frequently used design elements on content-heavy websites. Best practice search box interface design should have a combination of an input field and a submit button within proximity of each opther. The usability of this UI component is absolutely critical to the user experience. Search Boxes user interfaces should... Display the search field prominently Always add a magnifying-glass icon to a search box Put the search box where users expect to find it Always provide a button for the search box Clarify what users can search for Put it on every page Use a proper field size Use an auto-suggestion mechanism Follow these principles and make search work for users. Remember that users will have an expectation of a google type experience even if they aren't using google because they use it all the time! #uxdesign
-
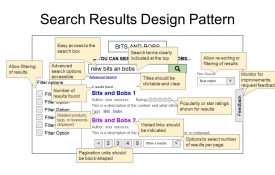
0 Search Results UX Design Pattern Guidelines
The search results page is the prime focus of the search experience. Use the following rules as a guideline for best practice search results design... Easy access to the search box Search terms clearly indicated at the top Titles should be clickable and clear Visited links should be indicated Pagination units should be block-shaped Related products, tags, or keywords displayed Enhancements to the search results will result in a better user experience because it helps the user to narrow down and filter the results how they want them. Add the following rules to your search results design to empower your users... Advanced search options accessible Allow re-sorting or filtering of results Results pages with “subscribe” options Popularity or star-ratings shown for results Options to select number of results per page Monitor for improvements, request feedback #uxdesign
-
0 10 UX Elements That Rule User Experience Design
A typical user will want all of these elements when performing a task. It is very important that we design with the user in mind... 1. Familiarity Accomplishing a goal should be obvious to the user, without confusion or explanation. 2. Responsiveness & Feedback Micro-tasks should be validated with feedback. Failure to provide appropriate feedback pulls focus away from the goal and forces an intense focus on micro-tasks. 3. Performance Performance issues indicate a poorly engineered product or technical malfunction. 4. Intuitiveness & Efficiency The degree to which the process of accomplishing a goal is obvious. 5. Helpfulness A solution may solve a business problem without considering user needs but in the end will have a negative effect on the business. 6. Relevant, Valuable Content Well timed, relevant content can increase user satisfaction and drive sales. (e.g. "Things you might also consider" when buying a product is a good example of this). 7. Internal Consistency The website, application or interface should handle similar tasks in similar ways. Consistent visual design gives the impression of a unified, well-organised, professional product. 8. External Consistency The visual appearance of a product should indicate its purpose and audience. This is also the case with branding standards. 9. Appropriateness To Context The use of language or imagery should be appropriate to the context. 10. Trustworthiness Issues that break engagement also injure the trustworthiness of a product.
-
0 UX = UI + UCD: What Is User Experience Design?
UI User Interface Design is the look and feel. It is the interaction layer between the user and the application, and in many cases, it concerns the interaction of a variety of users. Working on the user interface early on in the product development life cycle is vital because as far as the customer is concerned, the interface is the product. The user sees and interacts with the user interface, not the underlying back-end architecture of your application. Start by designing the interface first and then code the back-end that powers it, rather than building the back-end first and placing a wrapper over the top. UCD User Centered Design is the discipline of collecting and analysing User Requirements. User Requirements are the functions that the application should be able to perform from the perspective of the user. Principles Early Focus on Users and Tasks, A/B Testing to Refine the Application and Iterate, Iterate, Iterate. Gathering Understand the Product Domain, Profiles / Personas and Scenarios. Testing It is important to recruit participants that are similar to the profiles discovered from earlier field studies. This way you will be testing the correct type of user. Findings A prioritised list of user requirements to be acted upon and discussed. UX = UI +UCD These methods should be employed at every stage of the application life cycle... Interviews Surveys Card Sorting Group Task Analysis Wants and Needs Focus Groups Field Studies Only when you combine both UI and UCD do you achieve good results in the UX.
-
0 6 Signs A Project Is Heading For Failure And How To Prevent Them
General Assumptions “I know my users. You don’t need to talk to them”,A typical assumption from a stakeholder delivery mode. By assuming what users need and how they will behave will make the team lack empathy when building and delivering the final solution. Lack Of Shared Understanding When a shared understanding is not maintained it creates communication overhead, waste and churn, slow delivery and team demoralisation. A shared understanding will help the team build empathy. Communication Overheads When stakeholders and the team are not aligned and user goals are not understood, the strategy of the project is at risk of delivering average experiences to users. Stakeholders communicate successful outcomes for users.PMs build road maps for success so the team is rewarded. Waste And Churn If you build an average solution, deliver it, and fail to get user uptake, the outcome is failure. Feature factory sets in and a lot of time will be spent removing the features and functions from the delivered solution that users are not using. Expect a long bug list. Avoid waste by constantly usability testing the solution as early as possible with users, validating and refining it as required. Slow Delivery Because there is a lack in empathy the team gets frustrated not knowing what users are doing, the order of steps they are taking and the experience they are having. This leads to conversations, opinions and decisions made without any evidence. Foster empathy in the team by building the solution around user goals to provide value and obtain success. Team Demoralisation There is a higher likelihood for team members to get demoralised, perform average work or end up leaving when they are not empowered to make decisions. Syncing the team with stakeholders should happen frequently to enable to team to have input and feel empowered to contribute. Business Wants To Roll out new applications faster Respond quickly to new user demands Innovate with new technology to improve employee productivity IT Wants To Control costs and increase efficiency Provide choice and respond quickly Ensure security and compliance Business Factors Today Today digital businesses face new challenges. Limited skills, budget constraints and the pace of technology. Staff resources are limited hence the skills required are stretched or not available. Businesses can’t invest because budgets are declining. Things are moving fast, so businesses need to move fast and IT need to respond fast too. Things need to be made faster with less money and resources. Team Dynamics As user researchers we are constantly observing user behaviours, motivations and frustrations. We can use this skill to observe team members on a project and the dynamics involved. How well you provide outcomes for users depends entirely on the UX maturity of the organisation. If the organisation has low UX maturity you will find it very hard to change team dynamics.
-
0 The Business Benefits of User Experience Design
The benefits of UX go beyond improving the interface and the user experience: it benefits end users, developers and their companies. Satisfied customers are returning customers which lead to increased sales, longer use and more consumption. Unhappy customers lead to loss in sales due to poor design or the inability to find what they are looking for. Branding UX influences brand perception. A bad user experience damages the company brand. Users who have a bad experience with a brand typically tell others resulting in a reduction in use, customer retention and a bad reputation within the industry. An investment in UX creates positive experiences surrounding a brand. Costs UX reduces development and saves time. Making design changes cost 10x as much during the development phase and 100x as much after release. 80% of all software lifecycle costs occur in the maintenance phase. Productivity Usable systems are more intuitive, require less training and facilitate productive work. Although efficiency is not always the main issue in the usage of the system it is very important. If a system is designed to support how users prefer to work and is guided by UX principles it is generally more productive and efficient. Productivity improvements have the largest impact on work supporting systems. Increases Sales & Consumption Improves Brand Perception Reduces Development Costs Reduces Mantenance Costs Reduces Training Costs Improves Productivity UX is THE most powerful activity that brands can carry out to answer a range of questions which can be crucial to how their website or application performs.Questions around user perceptions, user behaviour, business processes, brand perception and customer research can be made through UX engineering.
-
0 How To Create An Elevator Pitch For Vision Alignment
An Elevator Pitch helps align a team around a shared vision and description of the product or service and its specialities. It creates a statement of what distinguishes the product from competitors. The Elevator Pitch Template For (Target Audience) who need (Opportunity), (Product/Service) provides (Solution), Unlike (Alternatives), it (Specialities). Elevator Pitch Elements Target Audience - Who are the users? Opportunity - What value are you giving to users? Product/Service - What is the product or service? Solution - What solution does it provide for users? Alternatives - What similar products or services exist? Specialities - How is the product or service special? Create a template and break into teams for everyone to participate!
-
0 In Demand: UX Designers & User Researchers
Move Into UX Design & User Research There’s a reason why companies that invest in great design outperform their competitors by over 200%. By employing User Experience (UX) Designers and User Researchers to create products and experiences that solve customer problems, brands can keep customers coming back, building essential revenue and loyalty. Consider A Future Of New Passions In my User Experience Design and User Research classes, you can skill up for an exciting UX career through training in research, design and collaboration with team members, real-world client projects and a dedicated trainer to help you get hired. All of my students who completed my classes got a job within one month. UX Might Be Your Next Move Check out my new syllabus to see the classes in more detail. My classes are designed to better help students get hired at top employers. Discover the kind of jobs you could get with UX skills... User Experience Designer User Researcher Information Architect Product Owner Content Designer Service Designer UX/UI Designer As you can see, UX has many transferable skills. Who Are My Classes For? Anyone who wants to move from their current job role to a career in User Experience or User Research UX Designers and User Researchers who want to demonstrate their knowledge of techniques, methods and core concepts in user experience Developers who want to learn techniques for designing more engaging systems Scrum Masters and Project Managers who want a full lifecycle process to ensure users are involved in their project Business Analysts who want effective tools for communicating requirements of users #uxjobs
-
0 15 Ways A Trainer Is Better Than A User Research Course
How Does Training Help Students? There are many reasons people choose a trainer. Some feel unable to attend classes. Others may find they are more receptive to working through struggles with another person. A Trainer can help strengthen subject comprehension, boost confidence, and build important learning skills. Trainers give students individualised attention that they do not get in a crowded classroom. This helps people who struggle to keep up, as well as those who aren’t challenged enough. 15 Ways A Trainer Is Better Individual and unique learning experience 121 attention Improves academic performance Improves attitude towards learning Encourages self-paced and self-directed learning Improves self-esteem and confidence Improves work and study habits Positive work space benefits Encourages independence and responsibility Helps overcome learning obstacles Encourages the freedom to ask questions Improves behavioural skills Increases ability to manage learning Challenges those who need it Prepares you for college The Problem With User Research Courses You learn theory and not real world application You may not be able to learn at your own pace You may not have the opportunity to go back on things You will not gain valuable tips from experienced trainers You will spend a lot of money and not learn a great deal So there you have it, my reasons why using a UR Trainer like me can benefit your career. #uxtraining #uxjobs
-
0 What Is User Research And What Do User Researchers Do?
I get asked this question a lot. I usually say that I help companies to observe their customers using their products in order to make improvements. However, there are so many other things that a User Researcher does. User Research in itself focuses on understanding user behaviours, needs and motivations. So what do User Researchers do? We use observation techniques, task analysis and other feedback methods We are not interested in finding out what users say or their opinions We are very interested in finding out what users do We gather assumptions from the team and stakeholders We open communication channels in projects We test and validate those assumptions with users and share findings We facilitate and foster alignment within teams to gain a shared understanding of user needs In a nutshell, User Researchers interface with users, stakeholders and teams acting as a central hub for relaying important findings back and forth throughout a project. When a project involves users interacting with a system, it is vital to understand users and their struggles, but it is equally important to see what value can be given to users and how that relates to a business benefit. User Researchers analyse both user needs and business benefits. #uxresearch